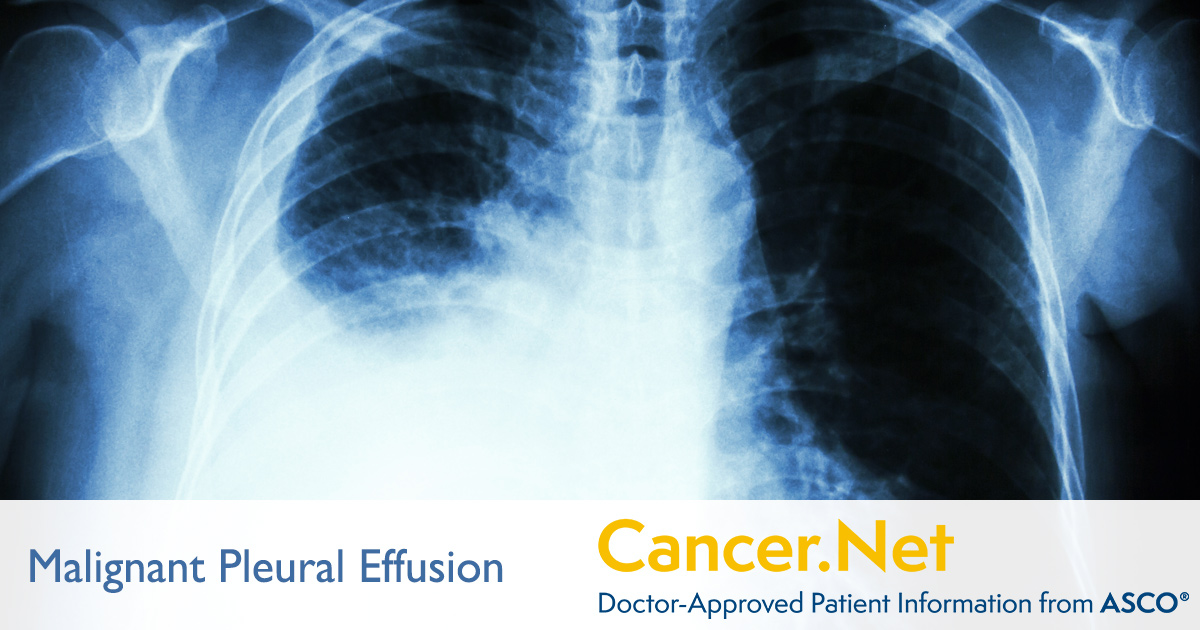
Lung cancer patients are particularly susceptible to malignant pleural effusion when fluid collects in the space between the lungs and the chest wall.
Cancer cells in fluid drained from lungs.
The types of cancer that are more likely to cause a pleural effusion are.
These sheets of tissue are called the pleura.
About half of people with cancer develop a pleural effusion when cancer grows in the pleural space it causes a malignant pleural effusion.
A malignant pleural effusion is a complication that involves the build up of fluid containing cancer cells between the membranes that line the lungs.
It occurs in around 7 to 23 of lung cancers but can also occur with other cancers such as breast cancer ovarian cancer leukemia and lymphomas.
An effusion can develop if cancer cells have spread into the pleura.
It can be diagnosed with the help of a chest x ray and draining out the unwanted fluid is possible.
It is observed that pleural effusion is mostly in seen in patients with cancers such as lung cancer breast cancer pleura cancer ovarian cancer and lymphomas.
This condition is a sign that the cancer has spread or metastasized to other areas of the body.
Treatment for fluid on the lung pleural effusion when cancer affects the lungs fluid can sometimes collect between the sheets of tissue that cover the outside of the lung and the lining of the chest cavity.
This area is called the pleural space.
This leaves an air filled space around.
Doctors call this fluid collection a pleural effusion.
Sometimes when the fluid is drained from the chest the lung cannot re expand to fill the chest cavity.